What are the terms of logarithm? Why are logarithms called logarithms? In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a given number x is the exponent to which another fixed number, the base b, must be raise to produce that number x. Sometimes a logarithm is written without a base, like this: log(100) This usually means that the base is really 10. It is called a common logarithm.
An old logarithm table and modern calculator. Logarithms come in the form. But what does mean? Before the days of calculators they were used to assist in the process of multiplication by replacing the operation of multiplication by addition. The logarithm of the multiplication of x and y is the sum of logarithm of x and logarithm of y. The logarithm for a base and a number is defined to be the inverse function of taking to the power, i. Logs undo exponentials.
Technically speaking, logs are the inverses of exponentials. The constant e and the natural logarithm. Learn what logarithms are and how to evaluate them. Introduction to logarithms.
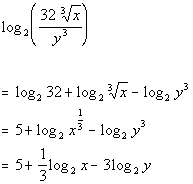
This is the currently selected item. Practice: Evaluate logarithms. The logarithm (log) is the inverse operation to exponentiation - and the logarithm of a number is the exponent to which the base - another fixed value - must be raised to produce that number. Specifically, a logarithm is the power to which a number (the base) must be raised to produce a given number.
A logarithm is the inverse of the exponential function. In other words, if we take a logarithm of a number, we undo an exponentiation. The three laws of logarithms.
That exponent is called a logarithm. We call the exponent the logarithm of with base 2. If the equation contains an exponent (that is, a variable raised to a power) it is an exponential equation. An exponent is a superscript number placed after a number. We built the LogRhythm NextGen SIEM Platform with you in mind.
Defending your enterprise comes with great responsibility. With intuitive, high-performance analytics and a seamless incident response workflow, your team will uncover threats faster, mitigate risks more efficiently, and produce measurable. Two kinds of logarithms are often used in chemistry: common (or Briggian) logarithms and natural (or Napierian) logarithms. The power to which a base of must be raised to obtain a number is called the common logarithm (log) of the number.
If we are given equations involving exponentials or the natural logarithm , remember that you can take the exponential of both sides of the equation to get rid of the logarithm or take the natural logarithm of both sides to get rid of the exponential. These allow expressions involving logarithms to be rewritten in a variety of different ways. The laws apply to logarithms of any base but the same base must be used throughout a calculation.
Nincsenek megjegyzések:
Megjegyzés küldése
Megjegyzés: Megjegyzéseket csak a blog tagjai írhatnak a blogba.